Aide et soutien
Aide et soutien
- FAQ's
- Glossary
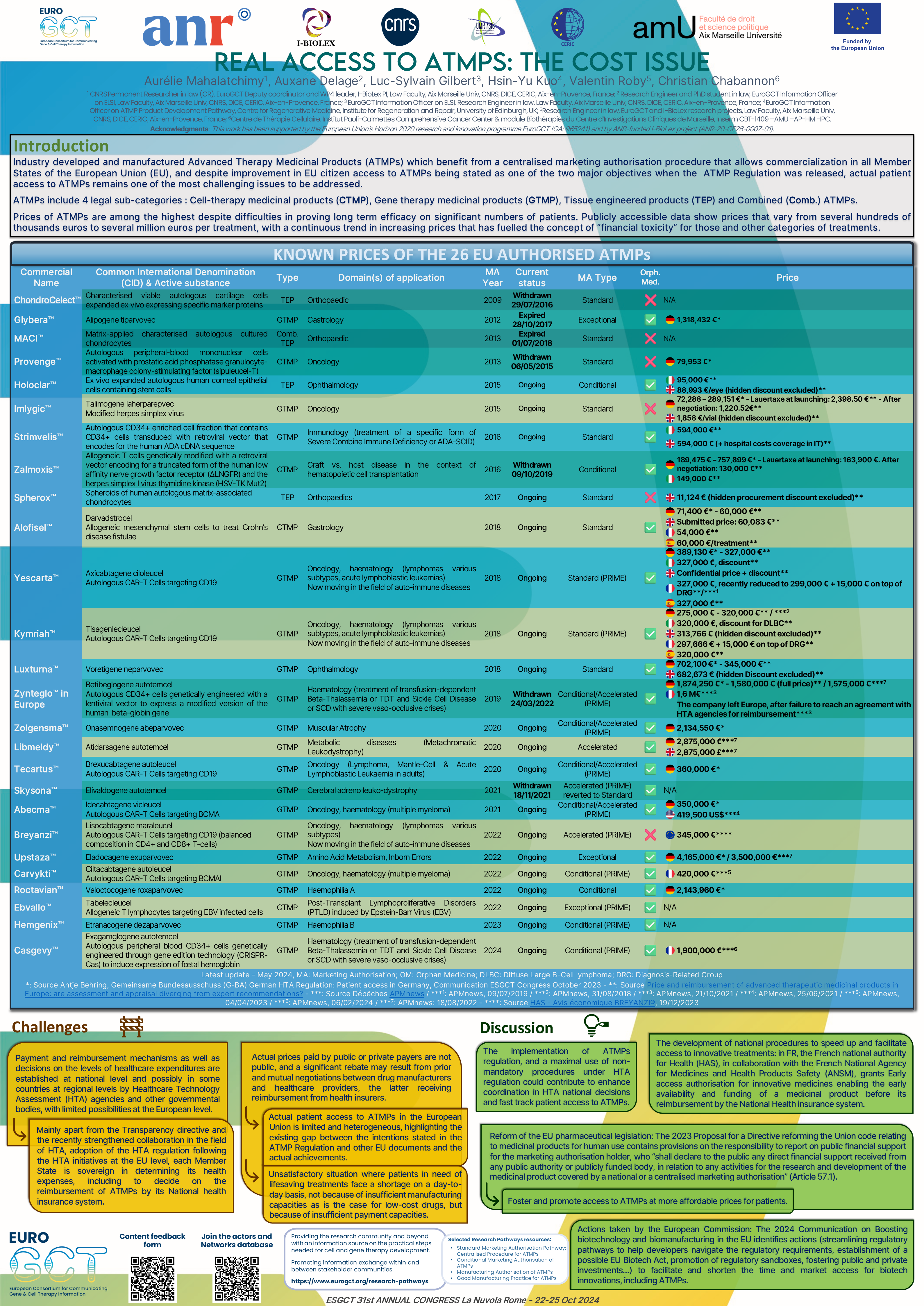
While industry developed and manufactured Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs) benefit from a centralised marketing authorisation procedure that allows commercialization in all Member States of the European Union (EU), and despite improvement in EU citizen access to ATMPs being stated as one of the two major objectives when the ATMP regulation was released, actual patient access to ATMPs remains one of the most challenging issues to be addressed. Prices of ATMPs are among the highest despite difficulties in proving long term efficacy on significant numbers of patients, although it is fair to acknowledge that cumulative costs of supportive and curative treatments that are administered on repeated occasions may fall in the same ranges. Publicly accessible data show prices that vary from several hundreds of thousands euros to several million euros per treatment, with a continuous trend in increasing prices that has fuelled the concept of “financial toxicity” for those and other categories of treatments. Payment and reimbursement mechanisms as well as decisions on the levels of healthcare expenditures are established at national and possibly in some countries at regional levels by Heathcare Technology Assesment (HTA) agencies and other governmental bodies, with limited possibilities at the European level. Indeed, mainly apart from the Transparency directive and the recently strengthened collaboration in the field of HTA thanks to the adoption of the HTA regulation following the HTA initiatives at the EU level, each Member States is sovereign in determining its health expenses, including to decide on the reimbursement of ATMPs by its National health insurance system. Actual prices paid by public or private payers are not public, and a significant rebate may result from prior and mutual negotiations between drug manufacturers and healthcare providers, the latter receiving reimbursement from health insurers. In addition, specific programs such as the “Early Access” (“Accès précoces”) program in France may speed up access to innovative treatments in some countries, thus favouring a category of EU citizens over others. Thus, actual patient access to ATMPs in the European Union is not only limited, but also heterogeneous, highlighting the existing gap between the intentions stated in the ATMP Regulation and other EU documents and the actual achievements; these diverse factors resulting in an unsatisfactory situation where patients in need of lifesaving treatments face a shortage on a day-to-day basis, not because of insufficient manufacturing capacities as is the case for low-cost drugs, but because of insufficient payment capacities. This poster first provides an overview of the known prices of the 26 ATMPs that have so far obtained a marketing authorisation in the EU. It also highlights what is regulated at the EU and at the National levels in this area. Finally, it suggests potential solutions to improve patients’ access to ATMPs.
The pdf file of this poster can be downloaded from the attachments section at the bottom of this page
Aurélie Mahalatchimy, EuroGCT Deputy coordinator and WP4 leader; UMR 7318 DICE CERIC, Aix-Marseille University, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Marseille, Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur, France
Auxane Delage, EuroGCT Information Officer on Ethical, Legal & Societal issues, Aix-en-Provence, France
Luc-Sylvain Gilbert, EuroGCT Information Officer on Ethical, Legal & Societal issues, Aix-en-Provence, France
Hsin-Yu Kuo, EuroGCT Project Manager - Research Information and Networks, Centre for Regenerative Medicine, Institute for Regeneration and Repair, Edinburgh University, UK
Valentin Roby, EuroGCT information officer on Ethical, Legal and Societal Issues
Christian Chabannon, Professor of Molecular Biology, MD, Centre de Thérapie Cellulaire. Institut Paoli-Calmettes Comprehensive Cancer Center & module Biothérapies du Centre d’Investigations Cliniques de Marseille, Inserm CBT-1409 –AMU –AP-HM -IPC